
Gel Electrophoresis
Agarose gel electrophoresis, method to separate mixed popular of DNA
Gel Electrophoresis
What is Gel Electrophoresis?
Gel Electrophoresis is an analytical technique used for resolve and analysis of macromolecules on the basis of their molecular weight and charge. Gel electrophoresis utilizes a gel as a sieving and anti-convective medium. This technique can be used to resolve complex DNAs (i.e., genomic DNA) for Southern blot analysis or to resolve the simpler digests of bacteriophage and plasmid clones for restriction enzyme site mapping and blotting or to observe the presence of PCR product.
How Gel Electrophoresis Works?
The principles of electrophoresis and electrophoretic separation are basic to many versatile methods of analytical separation. The fundamental of electrophoresis is the ability to separate charged molecules in an applied electric field. Biomolecules, which constantly associated with positive or negative electrical charges, has gain benefit to be separated by electrophoresis. Charged biomolecules migrate towards the electrode of opposite charge when electric supply is applied, due to the phenomenon of electrostatic attraction.
The migration and mobility speed of each type of molecules rely on several factors such as the size of molecules, molecular shape, net charge, charge/mass ratio, porosity and viscosity of the matrix in which the molecule moves through. Smaller fragments migrate faster than larger ones; the distance migrated on the gel varies inversely with the logarithm of the molecular weight. The size of fragments therefore can be determined by calibrating the gel, using known size standard, and comparing the distance of the unknown fragment that has migrated.
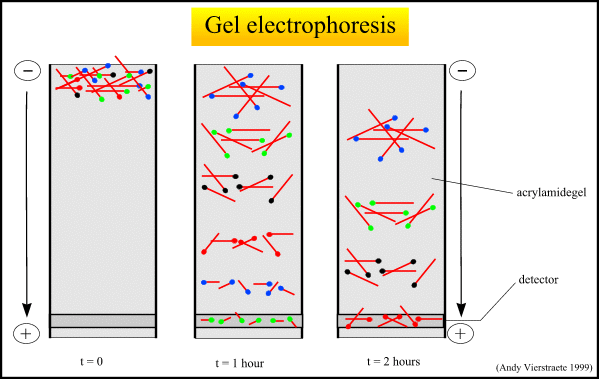
For instance, separation of DNA fragments by gel electrophoresis.The phosphate group in the DNA backbone carry negatively-charged phosphate which give rise to an overall negative charge of DNA molecule. Electric current are applied to separate different size of DNA fragments in a matrix. Smaller molecules migrate faster than the larger one due to smaller frictional force through the porous, sponge-like matrix.



